Your cart is empty.
shop now
Your cart is empty.
shop now
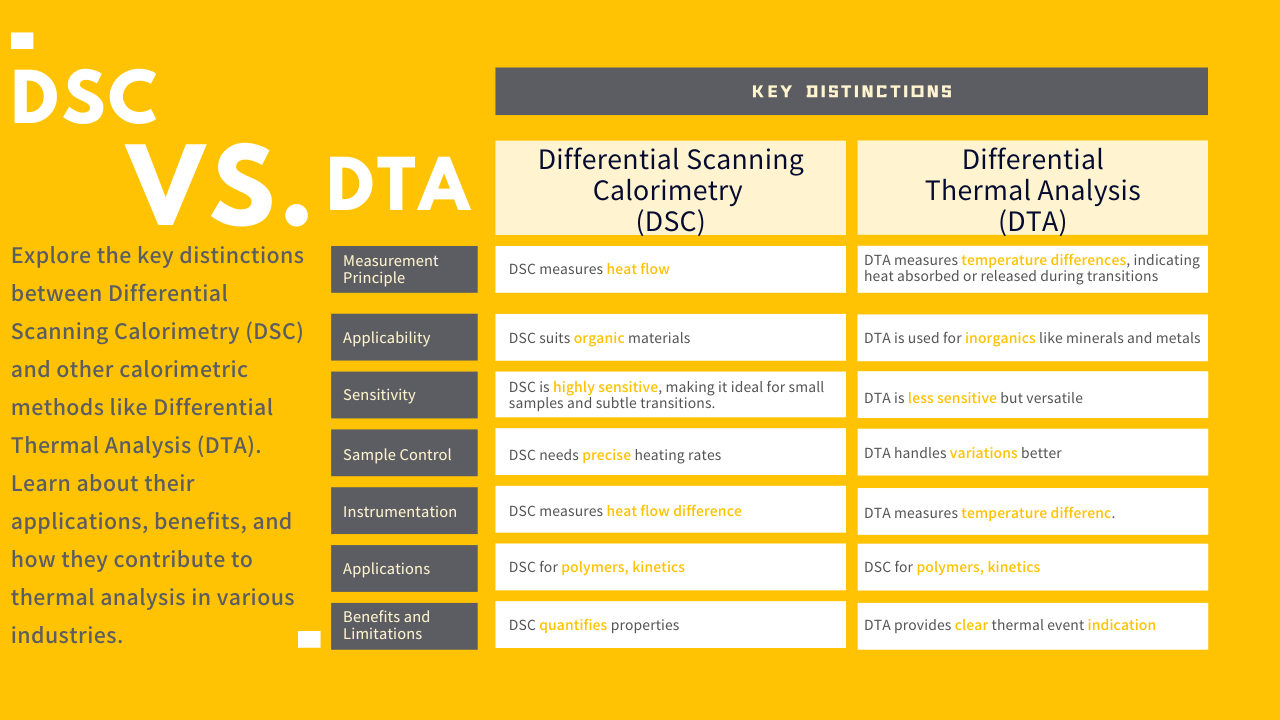
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) are both thermal analysis techniques used to investigate physical and chemical transformations in materials as they experience temperature changes. However, several key differences set them apart:
DSC measures the heat flow into or out of a sample as it undergoes temperature changes. This helps identify phase transitions, such as melting points and glass transitions. On the other hand, DTA measures the temperature difference between a sample and a reference material as they both experience the same temperature profile. This difference is indicative of the heat absorbed or released during phase transitions.
DSC finds extensive application in characterizing polymers, pharmaceuticals, foods, and various organic materials due to its sensitivity in detecting endothermic and exothermic transitions. DTA, with its broader scope, is suitable for studying inorganic materials, minerals, metals, and ceramics.
DSC is highly sensitive in detecting small energy changes, making it an excellent choice for analyzing minute samples and subtle transitions. DTA, while less sensitive, is valuable for its ability to study materials with irregular shapes or varying heat capacities.
DSC requires a well-controlled and uniform heating rate to obtain accurate results. In contrast, DTA is more forgiving in terms of heating rate variations, making it easier to work with in cases where precise control is challenging.
DSC instruments consist of a sample and reference compartment, both of which are maintained at the same temperature. Any difference in heat flow between the sample and reference is indicative of thermal events. DTA setups involve a sample and reference material, both subjected to identical temperature changes. The temperature difference between the sample and reference is measured, revealing thermal transitions.
DSC's sensitivity suits applications like polymer characterization, determination of reaction kinetics, and analysis of biomolecular interactions. DTA finds its niche in studying mineral compositions, phase diagrams, and identifying the purity of materials.
DSC's ability to quantify heat capacity and transition enthalpies provides valuable information about material properties. However, it may not distinguish overlapping transitions. DTA offers a clear indication of thermal events but lacks precise quantification of heat capacity.
Selecting between DSC and DTA depends on the material being analyzed, the nature of the transitions, and the desired information. Researchers often opt for both techniques to obtain a comprehensive understanding of complex materials.
A: While DSC and DTA serve similar purposes, their differences in sensitivity and applicability make them better suited for different types of materials and transitions.
A: No, both techniques have practical applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, materials science, and more.
A: DSC can reveal phase transitions, heat capacities, enthalpies, and even kinetic parameters of reactions.
A: Yes, DTA's broader scope and ability to handle irregular samples make it a preferred choice for inorganic materials.
A: DSC helps in drug development by analyzing polymorphic forms and stability, while DTA aids in characterizing excipients and detecting interactions.
A: DSC's high sensitivity allows it to detect subtle transitions, making it valuable in analyzing delicate processes.
In the realm of thermal analysis, Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) play indispensable roles in unraveling the mysteries of material behavior under changing temperatures. While DSC focuses on quantifying heat flow, DTA hones in on temperature differences. Their distinct applications, sensitivities, and benefits make them essential tools in diverse industries, each contributing uniquely to the world of thermal analysis.